Demystifying APIs: The Building Blocks of Modern Web Development
Introduction:
In the rapidly evolving world of web development, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) have emerged as the backbone of modern applications, facilitating seamless communication and data exchange between different systems. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of APIs, exploring what they are, how they work, and their crucial role in driving innovation and connectivity on the internet.
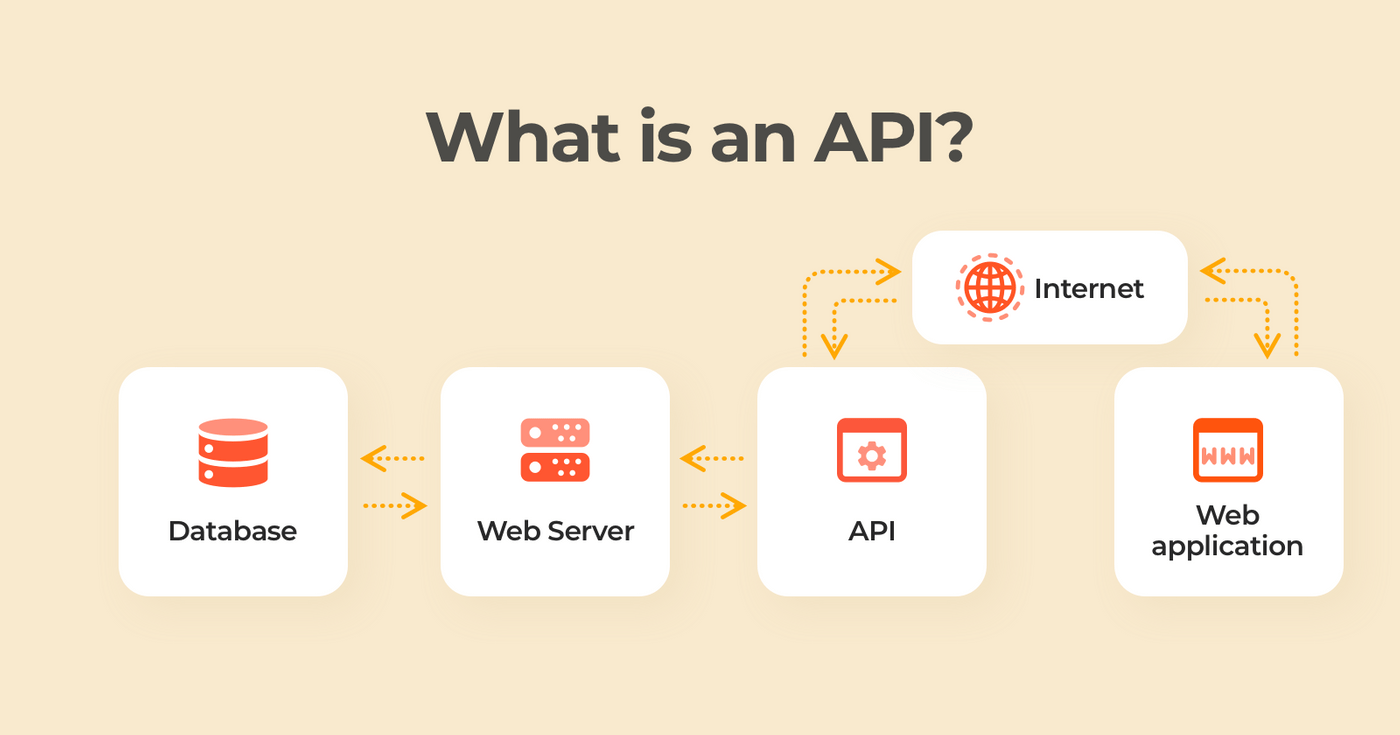
What is an API? At its core, an API is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate and interact with each other. It defines the methods and data formats applications can use to request and exchange information. APIs act as intermediaries, enabling developers to access specific features or data from external services or platforms without having to understand the underlying implementation.
Types of APIs:
Web APIs: Web APIs are designed for web applications and are accessible over the internet. They are typically based on RESTful (Representational State Transfer) architecture and use HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) for communication.
Operating System APIs: These APIs provide a way for software applications to interact with the underlying operating system, accessing features like file systems, hardware, and network services.
Library APIs: Library APIs expose sets of functions and methods within a programming language, allowing developers to access pre-built functionalities and components.
How APIs Work: When an application wants to access data or services from another application, it sends a request to the API endpoint, specifying the desired action and any required parameters. The API processes the request, performs the necessary actions, and sends back a response in a predefined format, such as JSON or XML. This process enables applications to share data and functionalities in a secure and controlled manner.
The Importance of APIs in Web Development:
Data Integration: APIs enable seamless data integration between applications, allowing developers to harness the power of external services and data sources to enhance their own applications.
Modularity and Reusability: APIs promote modularity by encapsulating functionalities into separate units, making it easier to maintain and reuse code.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: APIs provide a standardized way for applications to communicate, enabling cross-platform compatibility and integration.
Rapid Development: By leveraging APIs, developers can speed up development, as they can use existing functionalities rather than building everything from scratch.
Real-World Examples of APIs:
Social Media APIs: Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram offer APIs that allow developers to access user data, post updates, and interact with their services programmatically.
Payment Gateway APIs: Payment gateways like PayPal and Stripe provide APIs to process payments and manage transactions securely.
Google Maps API: The Google Maps API allows developers to integrate interactive maps and location-based services into their web and mobile applications.
Conclusion: APIs have revolutionized web development, opening up endless possibilities for creating innovative and interconnected applications. Whether it's accessing social media data, integrating payment gateways, or leveraging location-based services, APIs empower developers to create robust and feature-rich applications with ease. As the internet continues to evolve, APIs will remain fundamental building blocks for driving connectivity and collaboration in the digital age.
Note: This blog post provides an overview of APIs and their significance in web development. For more in-depth understanding and implementation, refer to official documentation and API usage guidelines.